Abstract
Case Report
Acute and chronic changes in massive Barium Sulfate aspiration in an infant who subsequently was diagnosed with severe Gastro-esophageal Reflux
Sevgi Pekcan*
Published: 19 June, 2017 | Volume 1 - Issue 1 | Pages: 003-008
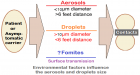
The barium is often used in radiocontrast examinations of the digestive system because of mucosal absorption is limited. Massive barium aspiration is a rare complication, especially when there is no anatomic or neurological deficit. The depending on barium concentration can cause various lung effects. When the literature is reviewed, barium aspiration may be asymptomatic or lethal in massive amounts. Rarely, large amounts of barium sulphate are aspirated into the lung, there is no literature study how often this is happening.
We present a case of massive barium aspiration in this subject. The case is related to a patient’s diagnostic esophagography who complaints swallowing problems. The massive barium aspiration couldn’t notice because of the absence of acute symptoms and surgical operation of gastrointestinal tract which the patient had undergone previously. When the patient applied our Pediatric Chest Diseases Polyclinic after three months, as a result of the examinations and deep research it was understood that the case was about massive barium aspiration. The patient was directed to our center because there was a radiological appearance of bone density signs on chest X-ray. Such a complaint was not reported by the family neighter in his biography, nor was written in the epicrisis. We will share acute and chronic changes in the lungs, diagnosis and treatment approaches of this case. The infant who has ileostomy was previously operated because of necrotizing enterocolitis. And also still has severe gastro-esophageal reflux and under conservative and medical treatment, a possible fundoplication surgery is planning.
Read Full Article HTML DOI: 10.29328/journal.jprr.1001002 Cite this Article Read Full Article PDF
Keywords:
Barium aspiration; Severe gastro-esophageal reflux; Infant
References
- Kakodkar K, Schroeder JW Jr. Pediatric dysphagia. Pediatr Clin North Am. 2013; 60: 969-977. Ref. : https://goo. gl/a2axYQ
- Darrow DH, Harley CM. Evaluation of swallowing disorders in children. OtolaryngolClin North Am. 1998; 31: 405-418. Ref. : https://goo. gl/zsQsPz
- Tamm I, Kortsik C. Severe barium sulfate aspiration into the lung: clinical presentation, prognosis and therapy Respiration. 1999; 66; 81-84 Ref. : https://goo. gl/FL68A3
- Nishikawa M. A study of aspiration in infants with recurrent pneumonia by Barium swallow examination using different concentrations of barium. Nihon IgakuHoshasen Gakkai Zasshi. 1994; 54: 129-136. Ref. : https://goo. gl/IAjSZm
- Chiu CY, Wong KS, Tsai MH. Massive aspiration of barium sulfate during an upper gastrointestinal examination in a child with dysphagia. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol. 2005; 69: 541-544. Ref. : https://goo. gl/6Usx8P
- Rasley A, Logemann JA, Kahrilas PJ, Rademaker AW, Pauloski BR, et al. Prevention of barium aspiration during videofluoroscopic swallowing studies: value of change in posture. American Journal of Roentgenology. 1993; 160: 1005-1009. Ref. : https://goo. gl/7Bezkw
- Lopez-Castilla J, Cano M, Munoz M, Soult JA, Andrés A, et al. Massive bronchoalveolar aspiration of barium sulphate during a radiologic study of the upper digestive tract. Pediatr Pulmonol. 1997; 24: 126-127 Ref. : https://goo. gl/R2UmJt
- Nelson SP, Chen EH, Syniar GM, Christoffel KK. Prevalence of symptoms of gastroesophageal reflux during infancy. A pediatric practice-based survey. Pediatric Practice Research Group. Arch Pediatr Adolesc Med. 1997; 151: 569-572. Ref. : https://goo. gl/82Un35
- Jackson M, Kapur N, Goyal V, Choo K, Sarikwal A, et al. Barium aspiration in an ınfant: a case report and review of management. Front Pediatr. 2014; 2: 37. Ref. : https://goo. gl/7tFNwS
- Roggli V, Shelburne J. Mineral pneumoconiosis. 2nd ed In: Dahl DH, Hammar SP. editors. editors. Pulmonary Pathology. New York: Springer-Verlag. 1998; 589-618.
- Voloudaki A, Ergazakis N, Gourtsoyiannis N. Late changes in barium sulphate aspiration: HRCT features. Eur Radiol. 2003; 13: 2226-2229. Ref. : https://goo. gl/DjEbYj
- Venkatraman B, Reluman IL, Abdul-Wahab A. High resolution computed tomography appearance of late sequela of barium aspiration in an asymptomatic young child. Saudi Med J. 2005; 26: 665-710. Ref. : https://goo. gl/DKJiPS
- Marchiori E, Souza A, Franquet T, Muller N. Diffuse high-attenuation pulmonary abnormalities: a pattern-oriented diagnostic approach on high-resolution CT. Am J Roentgenol. 2005; 184: 273-282. Ref. : https://goo. gl/k53l2b
- Nelson S, Christofordis A, Pratt P. Barium sulfate and bismuth subcarbonate suspension as bronchographic contrast media. Radiology. 1959; 72: 829-838. Ref. : https://goo. gl/RhBSUO
- Morton RE, Bonas R, Fourie B, Minford J. Videofluoroscopy in the assessment of feeding disorders of children with neurological problems. Dev Med Child Neurol. 1993; 35: 388-395. Ref. : https://goo. gl/xIv4ic
- Hiorns MP, Ryan MM. Current practice in paediatric videofluoroscopy. Pediatr Radiol. 2006; 36: 911-919. Ref. : https://goo. gl/yuh9yh
- Gray C, Sivaloganathan S, K. C. Simpkins. Aspiration of high-density barium contrast medium causing acute pulmonary inflammation-report of two fatal cases in elderly women with disordered swallowing. Clin Radiol. 1989; 40: 397-400 Ref. : https://goo. gl/AlqDJH
Figures:
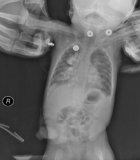
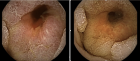
Figure 1
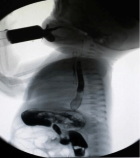
Figure 2
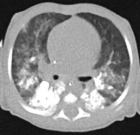
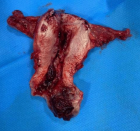
Figure 3
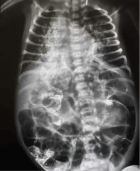
Figure 4
Similar Articles
-
Acute and chronic changes in massive Barium Sulfate aspiration in an infant who subsequently was diagnosed with severe Gastro-esophageal RefluxSevgi Pekcan*. Acute and chronic changes in massive Barium Sulfate aspiration in an infant who subsequently was diagnosed with severe Gastro-esophageal Reflux . . 2017 doi: 10.29328/journal.jprr.1001002; 1: 003-008
-
Asthma and pregnancy prevalence in a developing country and their mortality outcomesRaul Aguilar*,Jorge Martinez,Edgar Turcios,Victor Castro. Asthma and pregnancy prevalence in a developing country and their mortality outcomes. . 2021 doi: 10.29328/journal.jprr.1001031; 5: 088-093
Recently Viewed
-
Non-surgical Treatment of Verrucous Hyperplasia on Amputation Stump: A Case Report and Literature ReviewSajeda Alnabelsi*, Reem Hasan, Hussein Abdallah, Suzan Qattini. Non-surgical Treatment of Verrucous Hyperplasia on Amputation Stump: A Case Report and Literature Review. Ann Dermatol Res. 2024: doi: 10.29328/journal.adr.1001034; 8: 015-017
-
Investigating Anti-Bacterial and Anti-COVID-19 Virus Properties and Mode of Action of Pure Mg(OH)2 and Copper-infused Mg(OH)2 Nanoparticles and Coated Polypropylene SurfacesSaleh Alkarri*, Melinda Frame, John Cairney, Lee Maddan, Jin H Kim, Jonathan O Rayner. Investigating Anti-Bacterial and Anti-COVID-19 Virus Properties and Mode of Action of Pure Mg(OH)2 and Copper-infused Mg(OH)2 Nanoparticles and Coated Polypropylene Surfaces. Int J Clin Virol. 2024: doi: 10.29328/journal.ijcv.1001057; 8: 008-023
-
A Low-cost High-throughput Targeted Sequencing for the Accurate Detection of Respiratory Tract PathogenChangyan Ju, Chengbosen Zhou, Zhezhi Deng, Jingwei Gao, Weizhao Jiang, Hanbing Zeng, Haiwei Huang, Yongxiang Duan, David X Deng*. A Low-cost High-throughput Targeted Sequencing for the Accurate Detection of Respiratory Tract Pathogen. Int J Clin Virol. 2024: doi: 10.29328/journal.ijcv.1001056; 8: 001-007
-
About Efficiency of High-order Harmonic Generation in Attosecond PhysicsAng-Yang Yu*. About Efficiency of High-order Harmonic Generation in Attosecond Physics. Int J Clin Virol. 2024: doi: 10.29328/journal.ijcv.1001061; 8: 045-047
-
Coronaviruses have reached at Pre-elimination Stage with Nine Amino Acid Spike Deletions and Forty-nine Nucleotide 3’-UTR DeletionsAsit Kumar Chakraborty*. Coronaviruses have reached at Pre-elimination Stage with Nine Amino Acid Spike Deletions and Forty-nine Nucleotide 3’-UTR Deletions. Int J Clin Virol. 2024: doi: 10.29328/journal.ijcv.1001060; 8: 031-044
Most Viewed
-
Evaluation of Biostimulants Based on Recovered Protein Hydrolysates from Animal By-products as Plant Growth EnhancersH Pérez-Aguilar*, M Lacruz-Asaro, F Arán-Ais. Evaluation of Biostimulants Based on Recovered Protein Hydrolysates from Animal By-products as Plant Growth Enhancers. J Plant Sci Phytopathol. 2023 doi: 10.29328/journal.jpsp.1001104; 7: 042-047
-
Sinonasal Myxoma Extending into the Orbit in a 4-Year Old: A Case PresentationJulian A Purrinos*, Ramzi Younis. Sinonasal Myxoma Extending into the Orbit in a 4-Year Old: A Case Presentation. Arch Case Rep. 2024 doi: 10.29328/journal.acr.1001099; 8: 075-077
-
Feasibility study of magnetic sensing for detecting single-neuron action potentialsDenis Tonini,Kai Wu,Renata Saha,Jian-Ping Wang*. Feasibility study of magnetic sensing for detecting single-neuron action potentials. Ann Biomed Sci Eng. 2022 doi: 10.29328/journal.abse.1001018; 6: 019-029
-
Pediatric Dysgerminoma: Unveiling a Rare Ovarian TumorFaten Limaiem*, Khalil Saffar, Ahmed Halouani. Pediatric Dysgerminoma: Unveiling a Rare Ovarian Tumor. Arch Case Rep. 2024 doi: 10.29328/journal.acr.1001087; 8: 010-013
-
Physical activity can change the physiological and psychological circumstances during COVID-19 pandemic: A narrative reviewKhashayar Maroufi*. Physical activity can change the physiological and psychological circumstances during COVID-19 pandemic: A narrative review. J Sports Med Ther. 2021 doi: 10.29328/journal.jsmt.1001051; 6: 001-007

HSPI: We're glad you're here. Please click "create a new Query" if you are a new visitor to our website and need further information from us.
If you are already a member of our network and need to keep track of any developments regarding a question you have already submitted, click "take me to my Query."