Abstract
Research Article
Effect of diabetes mellitus on the Pulmonary Function Tests in Sudanese Diabetic Patients
Elmutaz H Taha, Ibrahim A Ali* and Omer A Musa
Published: 29 August, 2018 | Volume 2 - Issue 1 | Pages: 004-010
Background: Diabetes mellitus is a leading cause of illness and death. Pulmonary function test PFT has assumed a key role in epidemiological studies investigating the incidence, natural history and causality of lung disease.
Methods: A cross sectional study was conducted in The National Ribat Teaching Hospital and Jabir Abualiz Specialized Diabetes Center in Khartoum state to measure the respiratory muscle power in 31 diabetic patients (case group) and 30 non-diabetics patients (control groups). Pulmonary function tests were measured by using Digital Spirometer-Micro-Plus version.
Results: Lung function parameters between diabetic patients and their matched control group show no significant differences between the means of FVC, FEV1 and FEV1/FVC. However, diabetic patients showed significant reduction in PEFR.
Conclusions: Exercise and well control of diabetes helped in preserving normal respiratory muscle power. Continuous reasonable exercise with good control is highly recommended for all diabetics.
Read Full Article HTML DOI: 10.29328/journal.jprr.1001007 Cite this Article Read Full Article PDF
Keywords:
FEV1; FVC; PFT; Diabetes mellitus
References
- Ruppel GL. Pulmonary function testing. Trends and techniques. Resp Care Clinics. 1997; 3: 155-181.
- McKay, Ray T, Horvath, Edward P. Pulmonary function testing in industry. In: Occupational Medicine. Edited by Carl, Zenz, O, Bruca Dickerson. Edward, P. Horvath. Mosby London, Third edition, 1984; 229.
- Meo SA, Al-Drees AM, Arif M, Al-Rubean K. Lung function in type 2 Saudi diabetic patients. Saudi Med J. 2006; 27: 338-343. Ref.: https://tinyurl.com/yc96m4mx
- Davis WA, Knuiman M, Kendall P, Grange V, Davis M, et al. Glycemic exposure is associated with reduced pulmonary function in type 2 diabetes: the Fremantle Diabetes Study. Diabetes Care. 2014; 27: 752-757. Ref.: https://tinyurl.com/yc5v7wpr
- McKeever T, Weston P, Hubbard R, Fogarty A. Lung Function and Glucose Metabolism: An Analysis of Data from the Third National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey. Am J Epidemiol. 2005; 161: 546-556. Ref.: https://tinyurl.com/y8cy7fam
- Meo SA, Al Drees AM, Ahmed J, Ahmed Shah SF, Al-Regaiey K, et al. Effect of Duration of Disease on Ventilatory Function in an Ethnic Saudi Group of Diabetic Patients. J Diabetes Sci Technol. 2007; 1: 711-717. Ref.: https://tinyurl.com/y7a7mxja
- Ali MO, Begum S, Begum N, Ali T, Ferdousi S, et al. FVC, FEV1 and FEV1/FVC% in Type 2 Diabetes and Their Relationships with Duration of the Disease. J Bangladesh Soc Physiol. 2009; 4: 81-87. Ref.: https://tinyurl.com/y9ncwumb
- Park SW, Goodpaster BH, Strotmeyer ES, Rekeneire N, Harris TB, et al. Decreased Muscle Strength and Quality in Older Adults with Type 2 Diabetes: The Health, Aging and Body Composition Study. Diabetes. 2006; 55: 1813-1818. Ref.: https://tinyurl.com/ycardd5r
- Tobin MJ, Chadha TS, Jenouri G, Birch SJ, Gazeroglu HB, et al. Breathing patterns: 2. Diseased subjects. Chest. 1983; 84: 286-294. Ref.: https://tinyurl.com/ydgvp3wj
Figures:

Figure 1
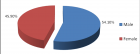
Figure 2
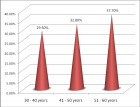
Figure 3
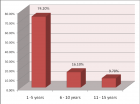
Figure 4
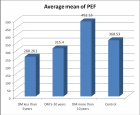
Figure 5

Figure 6
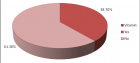
Figure 7
Similar Articles
-
Fluticasone furoate/Vilanterol 92/22 μg once-a-day vs Beclomethasone dipropionate/Formoterol 100/6 μg b.i.d. in asthma patients: a 12-week pilot studyClaudio Terzano*,Francesca Oriolo. Fluticasone furoate/Vilanterol 92/22 μg once-a-day vs Beclomethasone dipropionate/Formoterol 100/6 μg b.i.d. in asthma patients: a 12-week pilot study . . 2017 doi: 10.29328/journal.jprr.1001004; 1: 013-022
-
Effect of diabetes mellitus on the Pulmonary Function Tests in Sudanese Diabetic PatientsElmutaz H Taha,Ibrahim A Ali*,Omer A Musa. Effect of diabetes mellitus on the Pulmonary Function Tests in Sudanese Diabetic Patients . . 2018 doi: 10.29328/journal.jprr.1001007; 2: 004-010
-
COVID-19 disease with persistently negative RT-PCR test for SARS-CoV-2Sánchez Ríos Carla Paola*, Jiménez Cabrera Oscar Gabriel,Oropeza Lutzow Rebeca,Vázquez Rojas Hazel,Barreto Rodríguez José Omar,Guzmán-Casta Jordi,Guzmán-Huesca Jorge,Riera-Sala Rodrigo,Centeno Sáenz Gustavo Iván. COVID-19 disease with persistently negative RT-PCR test for SARS-CoV-2. . 2020 doi: 10.29328/journal.jprr.1001014; 4: 006-010
-
Pulmonary mucormycosis in post-pulmonary tuberculosis as an emerging risk factor: A rare case reportDivya Khanduja*,Naveen Pandhi. Pulmonary mucormycosis in post-pulmonary tuberculosis as an emerging risk factor: A rare case report. . 2021 doi: 10.29328/journal.jprr.1001026; 5: 059-063
-
COVID-19 and rhino-orbital mucormycosis – a case reportDilbag Singh*,Harveen Kaur,NC Kajal. COVID-19 and rhino-orbital mucormycosis – a case report. . 2021 doi: 10.29328/journal.jprr.1001032; 5: 094-096
-
Long-term results of 10 years of observation of cured cases of pulmonary tuberculosisBobokhojaev OI*. Long-term results of 10 years of observation of cured cases of pulmonary tuberculosis. . 2022 doi: 10.29328/journal.jprr.1001036; 6: 007-011
-
Clinical Approach to Immunotherapy-induced Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus: A Case of Pembrolizumab Associated Insulin-dependent Diabetes in a Patient with NSCLCNikolaos Ntertsos, George Christantoniou, Krystallia Kyrka, Persefoni Pezirkianidou, Vasileios Bikos, Papadaki Konstantina, Theodora Tsiouda*. Clinical Approach to Immunotherapy-induced Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus: A Case of Pembrolizumab Associated Insulin-dependent Diabetes in a Patient with NSCLC. . 2023 doi: 10.29328/journal.jprr.1001047; 7: 024-027
-
Effect of Azithromycin on Lung Function and Pulmonary Exacerbations in Children with Post-infectious Bronchiolitis Obliterans. A Double-blind, Placebo-controlled TrialCastaños Claudio*, Salin Maximiliano Felix, Pereyra Carla Luciana, Aguerre Veronica, Lucero Maria Belen, Bauer Gabriela, Zylbersztajn Brenda, Leviled Leonor, Gonzalez Pena Hebe. Effect of Azithromycin on Lung Function and Pulmonary Exacerbations in Children with Post-infectious Bronchiolitis Obliterans. A Double-blind, Placebo-controlled Trial. . 2024 doi: 10.29328/journal.jprr.1001052; 8: 009-014
-
Effectiveness of Intercostal Stretch Technique on Pulmonary Conditions: A Narrative ReviewKamrun Nahar Chowdhury*. Effectiveness of Intercostal Stretch Technique on Pulmonary Conditions: A Narrative Review. . 2024 doi: 10.29328/journal.jprr.1001059; 8: 048-052
Recently Viewed
-
Scientific Analysis of Eucharistic Miracles: Importance of a Standardization in EvaluationKelly Kearse*,Frank Ligaj. Scientific Analysis of Eucharistic Miracles: Importance of a Standardization in Evaluation. J Forensic Sci Res. 2024: doi: 10.29328/journal.jfsr.1001068; 8: 078-088
-
A study of coagulation profile in patients with cancer in a tertiary care hospitalGaurav Khichariya,Manjula K*,Subhashish Das,Kalyani R. A study of coagulation profile in patients with cancer in a tertiary care hospital. J Hematol Clin Res. 2021: doi: 10.29328/journal.jhcr.1001015; 5: 001-003
-
Additional Gold Recovery from Tailing Waste By Ion Exchange ResinsAshrapov UT*, Malikov Sh R, Erdanov MN, Mirzaev BB. Additional Gold Recovery from Tailing Waste By Ion Exchange Resins. Int J Phys Res Appl. 2024: doi: 10.29328/journal.ijpra.1001098; 7: 132-138
-
Prevalence of performance-enhancing drug use among gym members in Saudi Arabia, Riyadh: A cross-sectional surveyRawan Eskandarani*,Abdulaziz Alhamad,Saad Almodameg. Prevalence of performance-enhancing drug use among gym members in Saudi Arabia, Riyadh: A cross-sectional survey. J Sports Med Ther. 2022: doi: 10.29328/journal.jsmt.1001062; 7: 039-043
-
A Comparative Analysis of Traditional Latent Fingerprint Visualization Methods and Innovative Silica Gel G Powder ApproachBhoomi Aggarwal*. A Comparative Analysis of Traditional Latent Fingerprint Visualization Methods and Innovative Silica Gel G Powder Approach. J Forensic Sci Res. 2024: doi: 10.29328/journal.jfsr.1001063; 8: 040-046
Most Viewed
-
Evaluation of Biostimulants Based on Recovered Protein Hydrolysates from Animal By-products as Plant Growth EnhancersH Pérez-Aguilar*, M Lacruz-Asaro, F Arán-Ais. Evaluation of Biostimulants Based on Recovered Protein Hydrolysates from Animal By-products as Plant Growth Enhancers. J Plant Sci Phytopathol. 2023 doi: 10.29328/journal.jpsp.1001104; 7: 042-047
-
Sinonasal Myxoma Extending into the Orbit in a 4-Year Old: A Case PresentationJulian A Purrinos*, Ramzi Younis. Sinonasal Myxoma Extending into the Orbit in a 4-Year Old: A Case Presentation. Arch Case Rep. 2024 doi: 10.29328/journal.acr.1001099; 8: 075-077
-
Feasibility study of magnetic sensing for detecting single-neuron action potentialsDenis Tonini,Kai Wu,Renata Saha,Jian-Ping Wang*. Feasibility study of magnetic sensing for detecting single-neuron action potentials. Ann Biomed Sci Eng. 2022 doi: 10.29328/journal.abse.1001018; 6: 019-029
-
Pediatric Dysgerminoma: Unveiling a Rare Ovarian TumorFaten Limaiem*, Khalil Saffar, Ahmed Halouani. Pediatric Dysgerminoma: Unveiling a Rare Ovarian Tumor. Arch Case Rep. 2024 doi: 10.29328/journal.acr.1001087; 8: 010-013
-
Physical activity can change the physiological and psychological circumstances during COVID-19 pandemic: A narrative reviewKhashayar Maroufi*. Physical activity can change the physiological and psychological circumstances during COVID-19 pandemic: A narrative review. J Sports Med Ther. 2021 doi: 10.29328/journal.jsmt.1001051; 6: 001-007

HSPI: We're glad you're here. Please click "create a new Query" if you are a new visitor to our website and need further information from us.
If you are already a member of our network and need to keep track of any developments regarding a question you have already submitted, click "take me to my Query."